基于局地气候区的上海产业街区屋顶绿化近地降温效果
编号
lyqk010221


中文标题
基于局地气候区的上海产业街区屋顶绿化近地降温效果


作者单位
1. 同济大学建筑与城市规划学院 上海 20009;
2. 上海投资咨询集团有限公司智库研究中心 上海 200021


期刊名称
中国城市林业


年份
2023


卷号
21


期号
2


栏目名称
研究论文


中文摘要
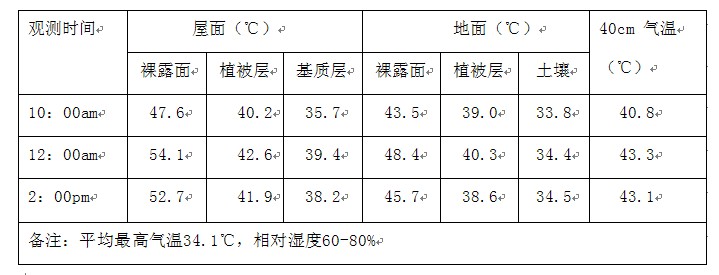
屋顶绿化是削减城市热岛强度的重要手段,其改善街区近地热环境的能力受街区形态的影响。文章基于局地气候区(Local Climate Zone, LCZ)框架,对上海4个优化类与转型类产业园样区中共115个产业街区进行形态分类,从各样区的主导类区中共选取12个典型街区,在上海夏季7月标准气象日条件下进行ENVI-met热环境模拟。结果表明:上海工业街区夏季白天近地温度最高的时刻与屋顶绿化降温效果最佳的时刻均为14∶00;上海夏季白天产业街区覆盖屋顶绿化前后近地热环境的改善具有统计显著性;铺设屋顶绿化后,LCZ5和LCZ3组街区的降温均值分别为-0.12℃与-0.07℃,且LCZ5类区的降温效果更佳。因此,从缓解热岛现象出发,上海产业园区若推进屋顶绿化建设,应优先考虑以LCZ5为主导形态类区的转型类产业园区。


关键词
屋顶绿化
近地热环境
局地气候区
产业街区
ENVI-met


基金项目
国家自然科学基金面上项目(52078350)


英文标题
Pedestrian Cooling Effect of Green Roofs on Industrial Blocks in Shanghai Based on Local Climate Zone


作者英文名
Luo Tianqing, Liu Yifan, Gong Xiuqi


单位英文名
1. College of Architecture and Urban Planning, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China;
2. Think Tank Research Center, Shanghai Investment Consulting Group Co., Ltd, Shanghai 200021, China


英文摘要
Rural plantscape is an important component of rural human settlements, and rural residents' perception of rural plantscape is of great significance for rural development. The paper selects 28 beautiful villages in Jinan, Shandong Province, and divides them into 3 types in accordance with the type of development, i.e., agriculture domination, business travel service and balanced development. Through field research, SD method and on-site interviews, rural residents' perception of plantscape in rural public spaces is evaluated, and its impact factors are studied, with a view to providing a reference for optimizing the plantscape design of the villages of different development types. The results show that the residents living in beautiful rural areas in Jinan are highly satisfied with the rural plantscape, and 70.94% of them hold a satisfactory attitude. There are differences in the SD evaluation of various types of rural areas. The agriculture villages are characterized with abundant space, few plant species, and small changes of plants in the four seasons. The business travel service dominated villages are characterized with rich plant species, large changes of plants in the four seasons, and insufficient interactive experience. The balanced development oriented villages are characterized with multiple plant species, natural wilderness, and rich in beauty. Atmosphere factors have the greatest impact on the perception of plantscape. The evaluation shows that the perception of rural plantscape is scored at 31.00, 21.81, and -31.53, respectively, for balanced development oriented village, business travel service dominated villages and agriculture dominated villages. Therefore, rural plantscapes in the villages of different development types have different characteristics and problems. The creation of rural plantscape should be adapted to local conditions to give more play to their advantages, fully consider local characteristics to address existing problems in a targeted manner, improve the rural living environment and improve residents' quality of life.


英文关键词
green roof;near-earth thermal environment;local climate zone;industrial block;ENVI-met


起始页码
58


截止页码
66


投稿时间
2022/12/2


作者简介
骆天庆(1970-),女,博士,副教授,研究方向为生态规划与设计。E-mail:luotq@tongji.edu.cn


通讯作者介绍
龚修齐(1996-),女,硕士,助理研究员,研究方向为规划研究。E-mail:xqgong@sicc.sh.cn


E-mail
xqgong@sicc.sh.cn


DOI
10.12169/zgcsly.2022.12.02.0001


参考文献
[1] SANTAMOURIS M.Regulating the damaged thermostat of the cities-Status,impacts and mitigation challenges[J].Energy and Buildings,2015,9(1):43-56.
[2] BESIR A B,CUCE E.Green roofs and facades:a comprehensive review[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2018,82:915-939.
[3] 龚修齐.简单式屋顶绿化改善街区热环境的效应模拟及优化研究:以上海市工业街区为例[D].上海:同济大学,2021.
[4] 韩林飞,柳振勇.城市屋顶绿化规划研究:以北京市为例[J].中国园林,2015,31(11):22-26.
[5] OKE T R.Street design and urban canopy layer climate[J].Energy and Buildings,1988,11(1/3):103-113.
[6] 郝又佳,陈岚,谭林,等.基于局地气候分区的成都街道空间冬季热舒适研究[J].中国城市林业,2023,21(1):27-36.
[7] 陈卓伟,邓昭华.基于多尺度地理加权回归的广州主城区街区形态与热岛强度关系研究[J].智能建筑与智慧城市,2021(10):13-17.
[8] 姜之点,彭立华,杨小山,等.街区尺度屋顶绿化热效应及其与城市形态结构之间的关系[J].生态学报,2018,38(19):7120-7134.
[9] 敖翔宇,谈建国,支星,等.上海城市热岛与热浪协同作用及其影响因子[J].地理学报,2019,74(9):1789-1802.
[10] 张菊,刘汉胡.2000-2017年上海市城市热岛效应时空变化分析[J].环境科学导刊,2020,39(3):36-39.
[11] 岑福康,韦冬,刘晓涛,等.上海市工业用地存量更新常态管理机制[J].上海国土资源,2017,38(4):9-11.
[12] 彭保发,石忆邵,王贺封,等.城市热岛效应的影响机理及其作用规律:以上海市为例[J].地理学报,2013,68(11):1461-1471.
[13] 骆天庆,苏怡柠,陈思羽.高度城市化地区既有建筑屋顶绿化建设潜力评析:以上海中心城区为例[J].风景园林,2019,26(1):82-85.
[14] 周岩,庄智,杨峰.城市街区形态对热岛强度及能耗的影响[J].住宅科技,2017,37(9):28-33.
[15] 骆天庆,龚修齐.工业化转型发展下城市工业景观的环境再生策略:上海典型案例调研与比较[J].景观设计学,2020,8(5):60-75.
[16] 董楠楠,吴静.基于ENVI-met模拟的屋顶绿化热环境影响[J].中国城市林业,2020,18(4):61-66.
[17] TAN M H,LI X B.Quantifying the effects of settlement size on urban heat islands in fairly uniform geographic areas[J].Habitat International,2015,49:100-106.
[18] STEWART I D,OKE T R.Local climate zones for urban temperature studies[J].Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,2012,93(12):1879-1900.
[19] 李悦.上海中心城典型街区空间形态与微气候环境模拟分析[D].上海:华东师范大学,2018.
[20] SIMON H,LINDÉN J,HOFFMANN D,et al.Modeling transpiration and leaf temperature of urban trees:a case study evaluating the microclimate model ENVI-met against measurement data[J].Landscape and Urban Planning,2018,174:33-40.
[21] 沈昭华,谭洪卫,吕思强,等.上海地区建筑能耗计算用典型年气象数据的研究[J].暖通空调,2010,40(1):89-94.
[22] 王蕾.工业厂房轻型屋顶绿化技术[J].工业建筑,2013,43(增刊1):58-60,73.
[23] 黄丽君,刘东,骆天庆,等.某绿化屋顶夏季热工性能模拟研究及验证[J].建筑科学,2018,34(8):44-50.
[24] 江斯达,占文凤,杨俊,等.局地气候分区框架下城市热岛时空分异特征研究进展[J].地理学报,2020,75(9):1860-1878.
[25] 林中立,徐涵秋.基于LCZ的城市热岛强度研究[J].地球信息科学学报,2017,19(5):713-722.
[26] 耿树丰,任嘉义,杨俊,等.局地气候区视角下的城市热环境研究[J].生态学报,2022,42(6):2221-2227.
[27] 赵恩灵,邓帆,李志远,等.基于局地气候区的武汉市地表热环境研究[J/OL].长江流域资源与环境:1-12[2022-11-23].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/42.1320.X.20221026.1108.002.html.
[28] SRIVANIT M,HOKAO K. Evaluating the cooling effects of greening for improving the outdoor thermal environment at an institutional campus in the summer[J].Building and Environment,2013,66:158-172.
[29] 张艳,鲍文杰,余琦,等.超大城市热岛效应的季节变化特征及其年际差异[J].地球物理学报,2012,55(4):1121-1128.
[30] 徐伟,杨涵洧,张仕鹏,等.上海城市热岛的变化特征[J].热带气象学报,2018,34(2):228-238.


PDF全文
浏览全文


-
相关记录
更多
- 基于局地气候分区的成都街道空间冬季热舒适研究 2023
- 绿色屋顶在高寒地区海绵化改造中的应用 2022
- 住区不同绿化组合比率的绿地热环境模拟 2022
- 热带城市典型棕榈类与阔叶类乔木热舒适效应对比 2022
- 基于ENVI-met模拟的屋顶绿化热环境影响 2020
- 基于ENVI-met的杭州夏季住宅热环境研究 2020
 打印
打印