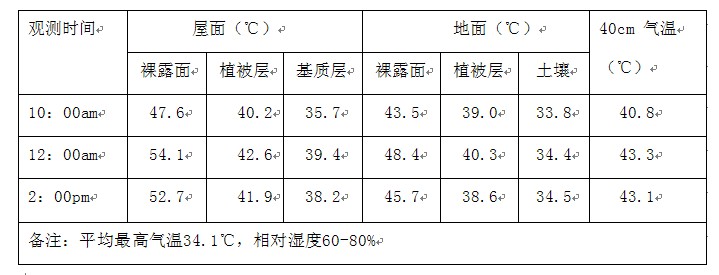
基于ENVI-met模拟的屋顶绿化热环境影响
编号
lyqk008395


中文标题
基于ENVI-met模拟的屋顶绿化热环境影响


作者单位
1. 同济大学建筑与城市规划学院 上海 200092;
2. 上海冠茵环境生态科技有限公司 上海 200092


期刊名称
中国城市林业


年份
2020


卷号
18


期号
4


栏目名称
研究论文


中文摘要
文章以同济大学四平路校区为研究对象,采用ENVI-met 4.4.2模拟4种方案(无绿化、地面绿化、屋顶绿化、地面绿化与屋顶绿化的组合绿化)时校园内温度分布特征,对比分析有地面绿化和无地面绿化情况下,7:00、12:00、20:00、1:00时屋顶绿化对室外行人高度(1.5m)和屋面高度(12.5m、17.5m)的气温影响。结果表明:1)校园无地面绿化时,屋顶绿化的降温效果较为微弱;2)校园有地面绿化时,屋顶绿化对环境气温的影响明显增强,尤其是行人高度的温度变化明显增大,且随着高度增加,影响逐渐减弱;3)校园有地面绿化时,12:00时屋顶绿化对建筑较少的开放区域降温效果明显好于建筑密度大的区域,而7:00、20:00和1:00时开放区域会出现升温现象。屋顶绿化除增加绿化总量外,也增加了绿色空间的连接性,有利于形成联系更为紧密的绿色空间网络,提高开放空间的热舒适性。


关键词
热环境
ENVI-met模拟
屋顶绿化


基金项目
德国联邦教育与研究部(BMBF)中德联合研究项目中德超大城市韧性发展模式下的绿色基础设施规划生态服务系统应用;自然资源部大都市区国土空间生态修复工程技术创新中心课题;城市更新区域三维数字模型技术研究及应用示范(19DZ1202300)


英文标题
Thermal Environment Effects of Green Roofs Based on ENVI-met Simulation


作者英文名
Dong Nannan, Wu Jing


单位英文名
1. College of Architecture and Urban Planning, Tongji University, Shanghai 200092, China;
2. Shanghai Guanyin Environmental Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai 200092, China


英文摘要
Taking the Siping Road Campus of Tongji University as the research object, the paper simulates the temperature distribution characteristics in the campus using ENVI-met 4.4.2 under four scenarios (no greening, ground greening, roof greening, and both ground and roof greening). The effects of roof greening at the outdoor pedestrian height (1.5 m) and roof height (12.5 m and 17.5 m) on temperature at 7:00 am,12:00 am, 20:00 pm and 1:00 am under the scenarios of having ground greening and having no ground greening are compared and analyzed. The results find that:1) The cooling effect of roof green is not obvious when ground greening is absent; 2) In the case that there is ground greening, roof green has enhanced influence on the ambient temperature, especially the temperature at outdoor pedestrian height which changes obviously, and the influence is gradually weak with the increase of height; and 3) When there is ground greening in campus, the cooling effect of green roof on the open area with less buildings at 12:00 is significantly better than that in the area with high building density, while the temperature of the open area will go up at 7:00 am, 20:00 pm and 1:00 am. In addition to increasing the total amount of greening, roof greening also increases the connectivity of green spaces, which is conducive to the formation of a more closely connected green space network and improve the thermal comfort of open spaces.


英文关键词
thermal environment;ENVI-met simulation;roof greening


起始页码
61


截止页码
66


投稿时间
2019/8/27


作者简介
董楠楠(1975-),男,博士,副教授,研究方向为风景园林技术创新及其性能化设计。E-mail:dongnannan@tongji.edu.cn


DOI
10.12169/zgcsly.2019.08.27.0001


参考文献
[1] STOCKER T F,QIN D,PLATTNER G K.Climate change 2013:the physical science basis-technical summary[R].Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC),2013:37.
[2] 岳晓蕾,林箐,杨宇翀.城市绿地对热岛效应缓解作用研究:以保定市中心城区为例[J].风景园林,2018,25(10):66-70.
[3] 李莹莹,邓雅云,陈永生,等.基于卫星遥感的合肥城市绿色空间对热环境的影响评估[J].生态环境学报,2018,27(7):1224-1233.
[4] LAI D Y,LIU W Y,GAN T T,et al.A review of mitigating strategies to improve the thermal environment and thermal comfort in urban outdoor spaces[J].Science of the Total Environment,2019,661:337-353.
[5] 周雪帆,陈宏,吴昀霓,等.基于移动测量的城市空间形态对夏季午后城市热环境影响研究[J].风景园林,2018,25(10):21-26.
[6] 李膨利,穆罕默德·阿米尔·西迪基,刘东云.基于遥感技术的城市下垫面参数与热环境关系的研究:以北京市朝阳区为例[J].风景园林,2019,26(5):18-23.
[7] 石满,陈健,吴迪,等.城市街区尺度地表热环境遥感监测与分析[J].红外技术,2019,41(1):84-91.
[8] 李小龙,杨英宝,曹利娟,等.基于遥感和CFD模拟的城市绿地形态对热环境的影响研究[J].遥感技术与应用,2016,31(6):1150-1157.
[9] ZHANG M,BAE W,KIM J.The effects of the layouts of vegetation and wind flow in an apartment housing complex to mitigate outdoor microclimate air temperature[J].Sustainability,2019,11(11):20.
[10] 沈滢洁,王成刚,曹乐,等.屋顶绿化对城市降温效应的模拟分析:以南京市为例[J].气象,2017,43(5):610-619.
[11] HWANG M K,BANG J H,KIM S,et al.Estimation of thermal comfort felt by human exposed to extreme heat wave in a complex urban area using a WRF-MENEX model[J].International Journal of Biometeorology,2019,63(7):927-938.
[12] 李佳慧,刘红年,马万里,等.城市小区建筑物和屋顶绿化对小区气象环境影响的数值模拟研究[J].气象科学,2017,37(1):41-50.
[13] LALOSEVIC M D,KOMATINA M S,MILOS M V,et al.Green roofs and cool materials as retrofitting strategies for urban heat island mitigation case study in Belgrade,Serbia[J].Thermal Science,2018,22(6):2309-2324.
[14] JIN C Q,BAI X L,LUO T,et al.Effects of green roofs' variations on the regional thermal environment using measurements and simulations in Chongqing,China[J].Urban Forestry & Urban Greening,2018,29:223-237.
[15] 戴菲,毕世波,郭晓华.基于ENVI-met的道路绿地微气候效应模拟与分析研究[J].城市建筑,2018(33):63-68.
[16] SUN S B,XU X Y,LAO Z M,et al.Evaluating the impact of urban green space and landscape design parameters on thermal comfort in hot summer by numerical simulation[J].Building and Environment,2017,123:277-288.
[17] TALEGHANI M,KLEEREKOPER L,TENPIERIK M,et al.Outdoor thermal comfort within five different urban forms in the Netherlands[J].Building and Environment,2015,83:65-78.
[18] 祝善友,高牧原,陈亭,等.基于ENVI-met模式的城市近地表气温模拟与分析:以南京市部分区域为例[J].气候与环境研究,2017,22(4):499-507.
[19] WILLMOTT C J.Some comments on the evaluation of model performance[J].Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society,1982,63(11):1309-1313.
[20] CHAI T F,DRAXLER R R.Root mean square error (RMSE) or mean absolute error (MAE)? -arguments against avoiding RMSE in the literature[J].Geoscientific Model Development,2014,7:1247-1250.
[21] ROSSO F,GOLASI I,CASTALDO V L,et al.On the impact of innovative materials on outdoor thermal comfort of pedestrians in historical urban canyons[J].Renewable Energy,2018,118:825-839.
[22] SALATA F,GOLASI L,PETITTI D,et al.Relating microclimate, human thermal comfort and health during heat waves:an analysis of heat island mitigation strategies through a case study in an urban outdoor environment[J].Sustainable Cities and Society,2017,30:79-96.
[23] MORAKINYO T E,DAHANAYAKE K W D K C,NG E,et al.Temperature and cooling demand reduction by green-roof types in different climates and urban densities:a co-simulation parametric study[J].Energy and Buildings,2017,145:226-237.
[24] LIN B R,LI X F,ZHU Y X,et al.Numerical simulation studies of the different vegetation patterns' effects on outdoor pedestrian thermal comfort[J].Journal of Wind Engineering And Industrial Aerodynamics,2008,96(10-11):1707-1718.
[25] WANG Y P,AKBARI H.The effects of street tree planting on urban heat island mitigation in montreal[J].Sustainable Cities and Society,2016,27:122-128.
[26] 姜之点,彭立华,杨小山,等.街区尺度屋顶绿化热效应及其与城市形态结构之间的关系[J].生态学报,2018,38(19):7120-7134.
[27] 陈宇,李骄娴,宋双双,等.南京市屋顶绿化室外热环境研究[J].中国城市林业,2017,15(3):44-48.


PDF全文
浏览全文


-
相关记录
更多
- 垂直绿化对城市微气候影响研究综述 2023
- 基于局地气候区的上海产业街区屋顶绿化近地降温效果 2023
- 绿色屋顶在高寒地区海绵化改造中的应用 2022
- 国际城市绿色空间热环境相关标准比较 2021
- 北京市屋顶绿化植物应用研究 2018
- 广州市节约型屋顶绿化常见有害生物的调查与防治 2018
 打印
打印