社区尺度下城市绿地对老年人健康的影响机制
编号
lyqk011077


中文标题
社区尺度下城市绿地对老年人健康的影响机制


作者单位
1. 武汉大学城市设计学院 武汉 430000;
2. 武汉市规划设计有限公司 武汉 430000


期刊名称
中国城市林业


年份
2023


卷号
21


期号
3


栏目名称
研究论文


中文摘要
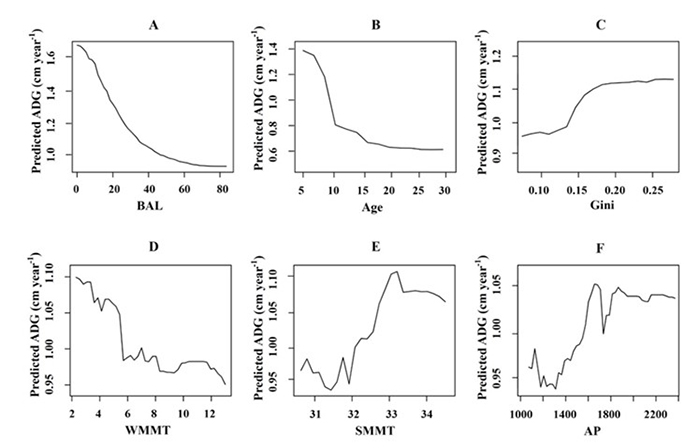
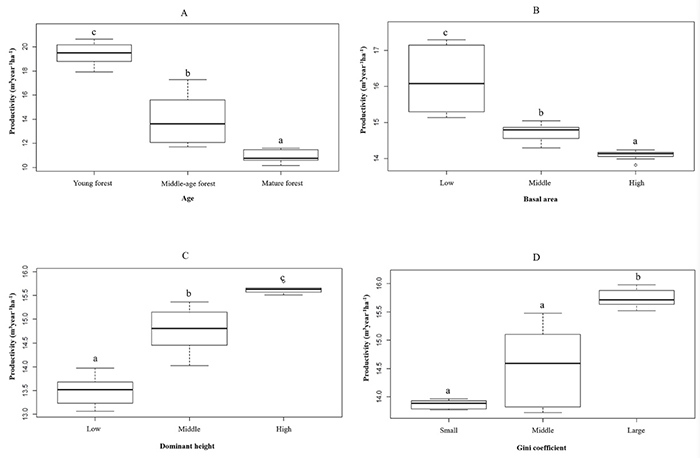
以武汉市主城区8个老龄化社区为研究对象,采取实地调研、问卷等方法获取60岁以上老年人的个体特征、老年人在社区及周边绿地的活动方式及活动后的身心感受;通过遥感影像和百度街景表征社区尺度下的绿地质量,利用结构方程模型研究绿地对老年人健康影响的作用机制。结果表明:1)在城市绿地作用于老年人健康的路径上,老年人个体特征的差异会导致不同的调节效应;2)在促进老年人健康的途径中,中介效应最强的是促进体力活动,其次是促进社会交往,最后是缓解压力;3)城市绿地的特征要素与老年人健康水平呈正相关,在影响老年人的健康水平上,社区植被覆盖度>社区缓冲区植被覆盖度>绿视率,城市绿地的可用性>可见性。


关键词
城市绿地
结构方程模型
影响机制
老年人健康
老龄化社区


英文标题
Influencing Mechanism of Urban Green Spaces on the Elderly's Health at the Community Scale


作者英文名
Song Jufang, Wu Jinning, Li Kunlin, Liu Xuejun


单位英文名
1. School of Urban Design, Wuhan University, WuHan 430000, China;
2. Wuhan Planning Design Co., Ltd, WuHan 430000, China


英文摘要
Taking 8 aging communities in the urban core area of Wuhan as the research objects, the study takes the methods of field investigations and questionnaires survey to obtain the individual characteristics of the elderly over 60 years old, their activities in the community and surrounding green spaces, and their physical and psychological conditions. Then the quality of green spaces at the community scale is characterized using remote sensing images and Baidu Street View, and the structural equation model is used to study the mechanism how green spaces influence the health of the elderly. The results show that:1) In the path that urban green spaces influence the health of the elderly, the differences of individual characteristics of the elderly will lead to different regulatory effects; 2) Among the pathways to improve the health of the elderly, increasing physical activity has the strongest mediating effect, followed sequentially by enhancing social interaction and reducing stress; and 3) The characteristic factors of urban green spaces are positively correlated with the health level of the elderly. The factors affecting the health of the elderly are ordered as community vegetation coverage > vegetation coverage in community buffer zone > green looking ratio, urban green space availability > visibility.


英文关键词
urban green space;structural equation model (SEM);influencing mechanism;elderly population health;aging community


起始页码
82


截止页码
87


投稿时间
2021/8/24


作者简介
宋菊芳(1972-),女,博士,副教授,研究方向为城市景观规划与设计。E-mail:sjufang@whu.edu.cn


通讯作者介绍
刘学军(1975-),男,博士,副教授,研究方向为城市交通与基础设施规划。E-mail:xjliu@whu.edu.cn


E-mail
xjliu@whu.edu.cn


DOI
10.12169/zgcsly.2021.08.24.0003


参考文献
[1] 骆天庆,傅玮芸.人口老龄化背景下的社区公园活动空间和游憩设施配置上海实例研究[J].风景园林,2016(4):96-101.
[2] 任泽平,熊柴,周哲.中国生育报告2019[J].发展研究,2019(6):20-40.
[3] 郭燕,王亮,严亚琼,等.武汉市老年人健康状况、身体活动与健康体适能的相关性[J].中国老年学杂志,2021,41(11):2420-2424.
[4] 穆光宗.不分年龄、人人健康:增龄视角下的健康老龄化[J].人口与发展,2018,24(1):11-13.
[5] 王晨羽.积极老龄化背景下北京城市公园适老化设计策略研究[D].北京:北京工业大学,2020.
[6] MALLER C,TOWNSEND M,PRYOR A,et al.Healthy nature healthy people:‘contact with nature’ as an upstream health promotion intervention for populations[J].Health Promotion International,2006,21(1):45-54.
[7] 陈玉洁,袁媛,周钰荃,等.蓝绿空间暴露对老年人健康的邻里影响:以广州市为例[J].地理科学,2020,40(10):1679-1687.
[8] 林雄斌,杨家文.北美都市区建成环境与公共健康关系的研究述评及其启示[J].规划师,2015,31(6):12-19.
[9] 王小月,杨东峰.建成环境如何影响老年人绿地使用频率:基于可达性和吸引力双重视角[J].中国园林,2020,36(11):62-66.
[10] 李树华,姚亚男,刘畅,等.绿地之于人体健康的功效与机理:绿色医学的提案[J].中国园林,2019,35(6):5-11.
[11] 陈璐瑶,谭少华,戴妍.社区绿地对人群健康的促进作用及规划策略[J].建筑与文化,2017(2):184-185.
[12] VÖLKER S,KISTEMANN T.The impact of blue space on human health and well-being:salutogenetic health effects of inland surface waters:a review[J].International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health,2011,214(6):449-460.
[13] 彭慧蕴,谭少华.城市公园绿地健康影响机制的概念框架建构[C]//共享与品质:2018中国城市规划年会论文集(13风景环境规划).北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2018.
[14] 陈广平.基于Ga2SFCA法的老年人医疗服务时空可达性研究[D].武汉:华中师范大学,2019.
[15] 姜玉培,甄峰,孙鸿鹄,等.健康视角下城市建成环境对老年人日常步行活动的影响研究[J].地理研究,2020,39(3):570-584.
[16] 姚尧,殷炜达,任亦询,等.空间分析视角下城市绿地与人体健康关系研究综述[J].风景园林,2021,28(4):92-98.
[17] BETHLEHEM J R,MACKENBACH J D,BEN-REBAH M,et al.The SPOTLIGHT virtual audit tool:a valid and reliable tool to assess obesogenic characteristics of the built environment[J].International Journal of Health Geographics,2014,13(6):52.
[18] LI X J,GHOSH D.Associations between body mass index and urban green streetscape in Cleveland,Ohio,USA[J].International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health,2018,15(10):2186.
[19] 彭慧蕴,谭少华.城市公园环境的恢复性效应影响机制研究:以重庆为例[J].中国园林,2018,34(9):5-9.
[20] 吴静.城乡居民幸福测量的结构方程模型[J].商业经济与管理,2009(4):66-72.
[21] 连帅磊,刘庆奇,孙晓军,等.手机成瘾与大学生拖延行为的关系:有调节的中介效应分析[J].心理发展与教育,2018,34(5):595-604.
[22] 董仁,李琳,韩汶,等.城市老年人出行行为特征研究:以昆明市为例[J].现代城市研究,2016(1):102-108.
[23] 周澜,胡家发,刘拥春.海南社区户外活动空间景观对老年人健康感知的影响[J].中国城市林业,2022,20(5):42-47.
[24] 黄海静,魏林颖.湿热地区老年人公园热舒适的环境因素[J].中国城市林业,2023,21(1):13-19.


PDF全文
浏览全文


-
相关记录
更多
- 城市鸟类群落与绿地关系研究进展 2022
- 城市绿地生态保健功能研究进展 2021
- 城市绿地恢复性感知研究进展 2021
- 城市绿地乔木固碳能力及碳抵消效果评估 2024
- 沈阳市夏季6种城市绿地景观对使用者身心恢复的影响 2024
- 北京城市绿地彩叶植物应用现状及优化策略 2023
 打印
打印