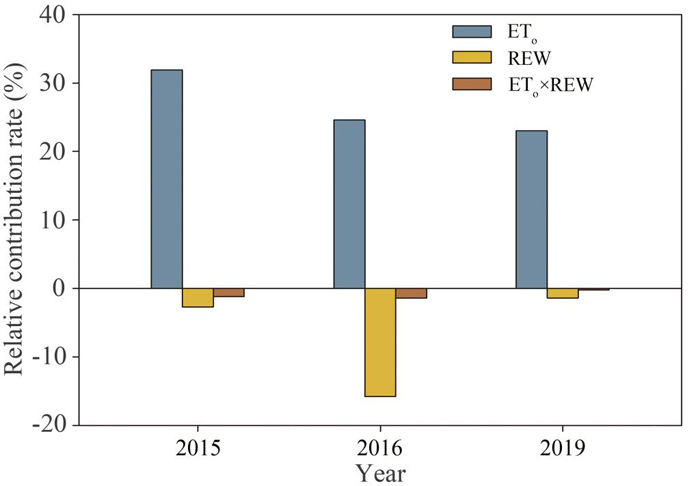
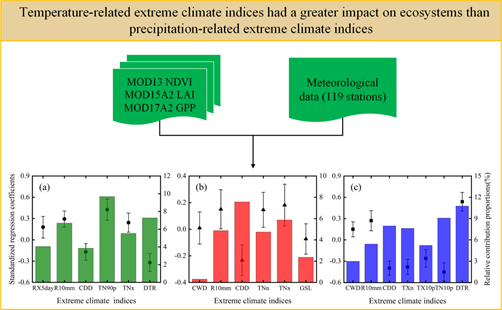
Advances of study on atmospheric methane oxidation (consumption) in forest soil
编号
zgly0000302951


文献类型
期刊论文


文献题名
Advances of study on atmospheric methane oxidation (consumption) in forest soil


学科分类
220.1040;森林土壤学


作者
WANGChen-rui
SHIYi
YANGXiao-ming
WUJie
YUEJin


作者单位
KeyLaboratoryofTerrestrialEcologicalProcess


母体文献
Journal of Forestry Research;林业研究: 英文版


年卷期
2003,14(3)


页码
230-238


年份
2003


分类号
S714
X16


关键词
森林土壤
氧化
大气甲烷
全球变暖
土壤碳氮比
土壤水分
树种


文摘内容
Next to CO2, methane (CH4) is the second important contributor to global warming in the atmosphere and global atmospheric CH4 budget depends on both CH4 sources and sinks. Unsaturated soil is known as a unique sink for atmospheric CH4 in terrestrial ecosystem. Many comparison studies proved that forest soil had the biggest capacity of oxidizing atmospheric CH4 in various unsaturated soils. However, up to now, there is not an overall review in the aspect of atmospheric CH4 oxidation (consumption) in forest soil. This paper analyzed advances of studies on the mechanism of atmospheric CH4 oxidation, and related natural factors (Soil physical and chemical characters, temperature and moisture, ambient main greenhouse gases concentrations, tree species, and forest fire) and anthropogenic factors (forest clear-cutting and thinning, fertilization, exogenou saluminum salts and atmospheric deposition, adding biocides, and switch of forest land use) in forest soils. It was believed that OH4 consumption rate by forest soil was limited by diffusion and sensitive to changes in water status and temperature of soil.CH4 oxidation was also particularly sensitive to soil C/N, Ambient CO2, CH4 and N2O concentrations, tree species and forest fire.In most cases, anthropogenic disturbances will decrease atmospheric CH4 oxidation, thus resulting in the elevating of atmos-pheric CH4. Finally, the author pointed out that our knowledge of atmospheric CH4 oxidation (consumption) in forest soil was insufficient. In order to evaluate the contribution of forest soils to atmospheric CH4 oxidation and the role of forest played in the process of global environmental change, and to forecast the trends of global warming exactly, more researchers need to studiesfurther on CH4 oxidation in various forest soils of different areas。


-
相关记录
更多
- 气候变化背景下全球陆地干湿变化研究综述 2023
- 冀北山地白桦林中小型土壤动物群落格局 2023
- 全球变暖对森林凋落物的影响 2023
- 宁南带状柠条林地根系及土壤水分养分分布特征 2023
- 干旱荒漠区白刺灌丛沙堆土壤温度及水分养分变化特征 2023
- 三峡库区典型茶园土壤水分对不同降雨模式的响应 2023
 打印
打印