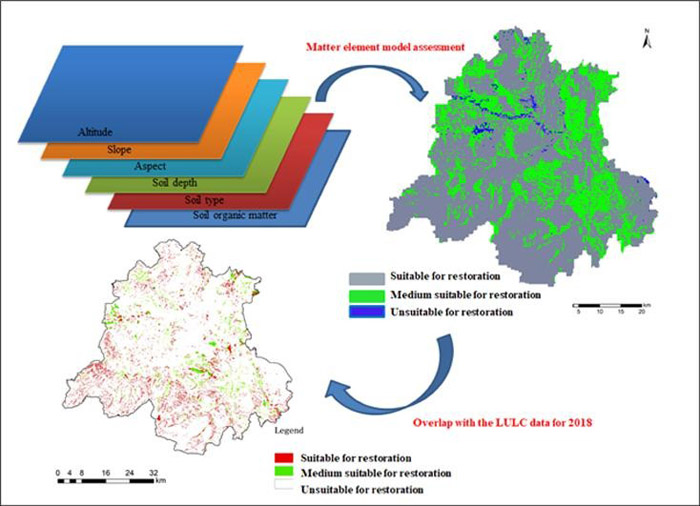
中国城市群生态系统及其定位观测研究站点的科学布局
编号
lyqk011256


中文标题
中国城市群生态系统及其定位观测研究站点的科学布局


作者单位
1. 国家林业和草原局科学技术司 北京 100714;
2. 中国林业科学研究院林业研究所 北京 100091;
3. 广东珠江口城市群生态系统国家定位观测研究站 广东东莞 523109


期刊名称
中国城市林业


年份
2023


卷号
21


期号
6


栏目名称
研究论文


中文摘要
城市是人类活动的中心,城市群是城市化发展的高级形态,城市群生态系统是城市群共同体协同发展的基础,城市群生态系统定位观测研究站的科学布局是城市群生态系统良性发展的基础保障。文章在分析我国城市群时空发展及其特点的基础上,论述了我国城市群生态系统的基本概念、发展演变、主要特点,并提出我国城市群生态系统定位观测研究站点的布设原则、布设方法、布设措施、布设展望,为我国城市生态文明和美丽中国建设提供重要科学依据。


基金项目
中央级公益性科研院所基本科研业务费专项资金(CAFYBB2020ZB008)


英文标题
Ecosystems in City Cluster and Science-based Layout of Ecosystem Positioning Observation and Research Stations in China


作者英文名
Li Shidong, Wang Cheng, Sun Zhenkai


单位英文名
1. Department of Science and Technology, National Forestry and Grassland Administration, Beijing 100714, China;
2. Research Institute of Forestry, Chinese Academy of Forestry, Beijing 100091, China;
3. Guangdong Pearl River Estuary City Cluster Urban Ecosystem National Observation and Research Station, Dongguan 523109, Guangdong, China


英文摘要
Cities are the centers of human activities. City clusters are the advanced development form of urbanization, and the city cluster ecosystem is the foundation for city cluster to engage coordinated development. The science-based layout of positioning observation and research stations of city cluster ecosystem is the basic assurance for the virtuous development of city cluster ecosystem. After analyzing the spatio-temporal development and characteristics of city clusters in China, this paper discusses the definition, evolution, and main characteristics of city cluster ecosystem in China, and proposes the principles, methods, measures and prospects of the layout of positioning observation and research stations of city cluster ecosystem in China. The study would provide an important scientific basis for developing urban ecological civilization and building a beautiful China.


英文关键词
city cluster;ecosystem;positioning observation and research;spatial layout


起始页码
63


截止页码
71


投稿时间
2023/12/8


作者简介
李世东(1966-),男,博士,教授级高级工程师,研究方向为生态保护修复、林草发展战略、智慧林业等。E-mail:eastworld@sohu.com


DOI
10.12169/zgcsly.2023.12.08.0002


参考文献
[1] UN-HABITAT.World cities report 2022:envisaging the future of cities[EB/OL].[2023-12-08].https://unhabitat.org/world-cities-report-2022-envisaging-the-future-of-cities.
[2] 国家统计局.中华人民共和国2022年国民经济和社会发展统计公报[J].中国统计,2023(3):12-29.
[3] 刘士林.改革开放以来中国城市群的发展历程与未来愿景[J].甘肃社会科学,2018(5):1-9.
[4] 高国力,李天健,孙文迁.我国城市群的基本特征、主要问题及对策思路(下)[J].中国发展观察,2018(2):34-36,41.
[5] 解振华.中国大百科全书-环境科学[M].北京:中国大百科全书出版社,2002.
[6] 陈利顶,孙然好,孙涛,等.城市群生态安全格局构建:概念辨析与理论思考[J].生态学报,2021,41(11):4251-4258.
[7] 国家林业局.全国森林城市发展规划(2018-2025年)[Z].2018.
[8] 李世东,王成,孙振凯.我国城市生态系统定位观测研究站的空间布局[J].中国城市林业,2023,21(3):52-59.
[9] 徐承红,张超.中国城市化发展道路及其新趋势[J].城市观察,2010(5):119-126.
[10] 宋冬林,姚常成.改革开放四十年:中国城镇化与城市群的道路选择[J].辽宁大学学报(哲学社会科学版),2018,46(5):45-52.
[11] 中华人民共和国国务院.国务院关于印发全国主体功能区规划的通知[EB/OL].(2010-12-21)[2023-12-08].https://www.gov.cn/gongbao/content/2011/content_1884884.htm.
[12] 人民出版社.中华人民共和国国民经济和社会发展第十四个五年规划和2035年远景目标纲要[M].北京:人民出版社,2021.
[13] 王成.中国城市森林建设范围与研究尺度[J].中国城市林业,2021,19(4):1-5.
[14] 王成.关于中国森林城市群建设的探讨[J].中国城市林业,2016,14(2):1-6.
[15] 王成,蔡春菊,陶康华.城市森林的概念、范围及其研究[J].世界林业研究,2004,17(2):23-27.
[16] 《中国林业百科全书》总纂委员会.中国林业百科全书-森林培育卷[M].北京:中国林业出版社,2022.
[17] 习近平.论坚持人与自然和谐共生[M].北京:中央文献出版社,2022.
[18] 王成.中国城市生态环境共同体与城市森林建设策略[J].中国城市林业,2016,14(1):1-7.
[19] 吴波.京津风沙源治理工程助力生态建设高质量发展[J].科学通报,2023,68(11):1284-1285.
[20] 国务院办公厅.国务院办公厅关于科学绿化的指导意见[J].中华人民共和国国务院公报,2021(17):178-182.
[21] 国家发展改革委,自然资源部.全国重要生态系统保护和修复重大工程总体规划(2021-2035年)[Z].2020.
[22] 李国平.多策并举促进我国城市群高质量发展[J].学术前沿,2022(22):16-28.
[23] 杨朝远,李培鑫.中国城市群可持续发展研究:基于理念及其评价分析[J].重庆大学学报(社会科学版),2018,24(3):1-12.
[24] 王成,张昶,金佳莉.森林城市群建设的评价指标[J].中国城市林业,2019,17(6):1-6.
[25] 王效科,欧阳志云,任玉芬,等.中美城市生态系统长期监测的内容和方法.地球科学进展,2014,29(5):617-623.


PDF全文
浏览全文


-
相关记录
更多
- 我国城市生态系统定位观测研究站的空间布局 2023
- 基于混沌论的绿地系统布局多情景优化模拟 2020
- 河岸带韧性植物群落研究综述 2019
- 乡村庭院植物景观演变特征研究 2018
- 近自然小流域森林经营理论与实践 2016
- 珠海森林城市建设总体规划研究 2016
 打印
打印