热带湿季不同海拔林分的空气负离子特征及微气候效应
编号
lyqk011400


中文标题
热带湿季不同海拔林分的空气负离子特征及微气候效应


作者单位
1. 海南大学热带农林学院 海口 570228;
2. 海南大学生态与环境学院 海口 570228;
3. 热带特色林木花卉遗传与种质创新教育部重点实验室 海口 570228


期刊名称
中国城市林业


年份
2024


卷号
22


期号
1


栏目名称
专题:城市森林康养


中文摘要
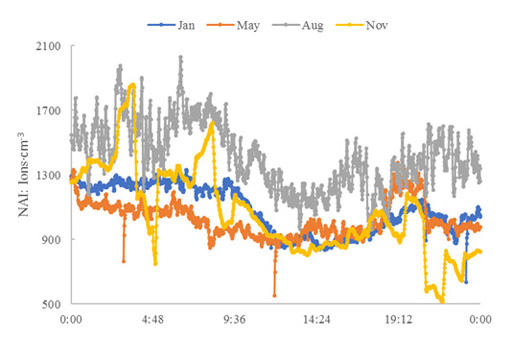
为研究湿季不同林分空气负离子浓度的变化规律及其影响因素,选取三亚南岛森林康养基地同一海拔的4种林分类型和不同海拔梯度的常绿阔叶林、槟榔林为研究对象,采用空气负氧离子检测仪及气象记录仪在7—9月份进行数据监测,并对数据进行单因素方差分析、多重比较及相关性分析。结果表明:1)4种林分空气负离子浓度日变化均呈双峰型,不同林分间存在极显著差异,其均值从高到低的排序为橡胶林>常绿阔叶林>槟榔林>母生林,群落结构越复杂、郁闭度越高,负离子变异性越小。2)受植物自身生理特性、群落结构等的影响,不同林分空气负离子浓度与微气候具有不同的线性相关关系。3)常绿阔叶林、槟榔林负离子浓度与海拔呈显著性负相关,槟榔林负离子浓度变异系数与海拔呈正相关。因此,4种不同林分中,橡胶林的康养效果最佳,其次为常绿阔叶林,今后在森林康养旅游中,可优先选择这两种林分进行游憩。


基金项目
海南省自然科学基金(421QN200,421MS015)


英文标题
Negative Air Ions Characteristics and Microclimate Effects of Forest Stands at Different Elevations in Tropical Wet Season


作者英文名
Si Yanping, Chen Jun, Cao Lingyi, He Rongxiao


单位英文名
1. College of Tropical Agriculture and Forestry, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China;
2. College of Ecology and Environment, Hainan University, Haikou 570228, China;
3. Key Laboratory of Genetics and Germplasm Innovation of Tropical Special Forest Trees and Ornamental Plants, Ministry of Education, Haikou 570228, China


英文摘要
In order to study the changing pattern of negative air ion concentration at different stands in wet season and its influencing factors, 4 types of forest at the same altitude as well as evergreen broad-leaved forest and Areca catechu forest at different altitudes are selected in Nandao Forest-based Health Base, and the data about negative air ion are monitored from July to September using negative air ion detector and aerograph and analyzed with one-way ANOVA, multiple comparisons and correlation analysis. The results show that: 1) The diurnal variations of negative air ion concentration in the types of forest stand present a bimodal pattern, and there are extremely significant differences among different stands. The mean values are ranked from high to low as rubber plantation > evergreen broad-leaved forest > A. catechu forest > Homalium hainanense forest. The more complex the community structure and the higher the canopy density, the smaller the negative air ion variability; 2) Affected by the physiological characteristics and community structure of plants, the concentrations of negative air ions in different stands have different linear correlations with microclimate; and 3) The negative air ion concentrations in the evergreen broad-leaved forest and A. catechu forest are significantly negatively correlated with the altitude, and the variation coefficient of negative air ion concentration in A. catechu forest is positively correlated with the altitude. It can be seen that among the 4 types of forest stands, the rubber forest has the best effect in forest-based health and wellness, followed by the evergreen broad-leaved forest. Therefore, the two types of forests can be preferred for recreation activities to achieve forest-based health.


英文关键词
forest therapy;negative air ion;microclimate;plant community;vegetation type


起始页码
111


截止页码
117


投稿时间
2022/4/21


作者简介
司艳萍(1994-),女,硕士,研究方向为森林康养景观设计。E-mail:1074166395@qq.com


通讯作者介绍
何荣晓(1987-),男,博士,讲师,研究方向为城市绿地生态景观规划。E-mail:rx.he@hainanu.edu.cn


E-mail
rx.he@hainanu.edu.cn


DOI
10.12169/zgcsly.2022.04.21.0001


参考文献
[1] 王一荃,周璋,李意德,等.不同热带森林空气负离子浓度评价研究[J].生态环境学报,2021,30(5):898-906.
[2] WANG H,WANG B,NIU X,et al.Study on the change of negative air ion concentration and its influencing factors at differentspatio-temporal scales[J].Global Ecology and Conservation,2020,23:e01008.
[3] 彭巍,李明文,王慧,等.空气负离子国内外研究进展及其在森林康养方面的积极作用综述[J].温带林业研究,2020,3(3):11-14,54.
[4] 章志攀,俞益武,孟明浩,等.旅游环境中空气负离子的研究进展[J].浙江林学院学报,2006,23(1):103-108.
[5] 高铭聪,蒋文伟,金竹秀,等.西径山森林公园夏季空气负离子日变化[J].浙江农林大学学报,2011,28(4):667-673.
[6] 周斌,余树全,张超,等.不同树种林分对空气负离子浓度的影响[J].浙江农林大学学报,2011,28(2):200-206.
[7] 刘宇,王晓立,董蓉,等.供暖季4种林地空气负离子浓度变化及其与主要影响因子的关系[J].江苏农业科学,2016,44(12):248-252.
[8] 曾曙才,苏志尧,陈北光.我国森林空气负离子研究进展[J].南京林业大学学报(自然科学版),2006,30(5):107-111.
[9] 邵海荣,贺庆棠.森林与空气负离子[J].世界林业研究,2000,13(5):19-23.
[10] 马璨,楚医峰,殷晓轩.空气负离子临床应用与中医环境养生[J].中医药临床杂志,2016,28(5):628-630.
[11] 冯鹏飞,于新文,张旭.北京地区不同植被类型空气负离子浓度及其影响因素分析[J].生态环境学报,2015,24(5):818-824.
[12] 赵庆,钱万惠,唐洪辉,等.广东省云勇森林公园6种林分保健功能差异比较[J].浙江农林大学学报,2018,35(4):750-756.
[13] 刘欣欣,华超,张明如,等.千岛湖姥山林场不同森林群落空气负离子浓度的比较[J].浙江农林大学学报,2012,29(3):366-373.
[14] 司婷婷,罗艳菊,毕华,等.吊罗山热带雨林空气负离子含量变化特征初探[J].林业资源管理,2015(4):139-144.
[15] YAN X J,WANG H R,HOU Z Y,et al.Spatial analysis of the ecological effects of negative air ions in urban vegetated areas:a case study inMaiji,China[J].Urban Forestry & Urban Greening,2015,14(3):636-645.
[16] 余海,辛学兵,裴顺祥,等.九龙山林缘地区空气负离子浓度变化特征及与气象因素关系[J].生态科学,2018,37(6):191-198.
[17] 赵怡宁,史常青,许荡飞,等.崇礼区典型林分空气负离子浓度及影响因素[J].林业科学研究,2018,31(3):127-135.
[18] LUO L H,SUN W,HAN Y J,et al.Importance evaluation based on random forest algorithms:insights into the relationship between negative air ions variability and environmental factors in urban green spaces[J].Atmosphere,2020,11(7):706.
[19] 孙文,韩玉洁,殷杉.城市公园不同植物群落内空气负离子变异格局及影响因素[J].华东师范大学学报(自然科学版),2021(2):151-159.
[20] 李少宁,王燕,张玉平,等.北京典型园林植物区空气负离子分布特征研究[J].北京林业大学学报,2010,32(1):130-135.
[21] 关昶翔,许新宇,林双毅,等.福州国家森林公园空气负氧离子浓度变化特征与影响因素[J].中国城市林业,2022,20(6):79-84.
[22] 马荣,王志高,黄玉洁,等.午潮山国家森林公园秋季空气负离子浓度及影响因素[J].森林与环境学报,2021,41(1):26-34.
[23] 许涵,李意德,骆土寿,等.达维台风对海南尖峰岭热带山地雨林群落的影响[J].植物生态学报,2008,32(6):1323-1334.
[24] 黄向华,王健,曾宏达,等.城市空气负离子浓度时空分布及其影响因素综述[J].应用生态学报,2013,24(6):1761-1768.
[25] 王薇,陈明,夏斯涵.高密度城市住区绿地空气负离子浓度分布特征及其与微气候关系[J].生态环境学报,2020,29(7):1367-1376.
[26] 吴楚材,郑群明,钟林生.森林游憩区空气负离子水平的研究[J].林业科学,2001,37(5):75-81.
[27] 蒙晋佳,张燕.地面上的空气负离子主要来源于植物的尖端放电[J].环境科学与技术,2005,28(1):112-113,120.
[28] 吴楚材,钟林生,刘晓明.马尾松纯林林分因子对空气负离子浓度影响的研究[J].中南林学院学报,1998,18(1):70-73.
[29] 刘新,吴林豪,张浩,等.城市绿地植物群落空气负离子浓度及影响要素研究[J].复旦学报(自然科学版),2011,50(2):206-212.
[30] 刘端,白志强,韩燕梁.喀纳斯国家级森林公园景区夏秋季空气负离子浓度变化特征[J].西北林学院学报,2015,30(3):253-257.
[31] 彭琳玉,许方岳,王立夫,等.九连山国家森林公园负氧离子浓度时空变化及影响要素研究[J].西北林学院学报,2020,35(5):233-239.
[32] 李少宁,李嫒,鲁绍伟,等.北京西山国家森林公园中空气负离子浓度与气象因子的相关性研究[J].生态环境学报,2021,30(3):541-547.
[33] 张嘉昕,邹嘉南.江西大岗山负离子浓度与气象因子之间的响应关系[J].气象与减灾研究,2021,44(1):51-57.
[34] 王淑娟,王芳,郭俊刚,等.森林空气负离子及其主要影响因子的研究进展[J].内蒙古农业大学学报(自然科学版),2008,29(1):243-247.
[35] 刘开明,郑智,龚大洁.物种丰富度的垂直分布格局及其形成机制[J].生态学杂志,2017,36(2):541-554.


PDF全文
浏览全文


-
相关记录
更多
- 基于森林康养理念的城市公园规划设计 2023
- 森林康养区内颗粒物浓度的影响因素——以北京松山自然保护区为例 2023
- 垂直绿化对城市微气候影响研究综述 2023
- 作品名称:五龙绿谷森林康养基地总体规划设计 2022
- 中国森林康养资源利用与产品开发 2022
- 九龙峰自然保护区不同森林类型乔木层树种组成及其动态变化 2022
 打印
打印